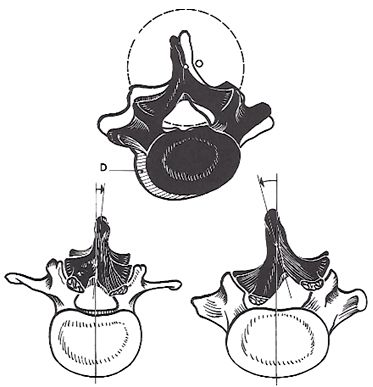
Lumbar Vertebral Column and General Anatomy
The Lumbar Vertebral Column, General Anatomy
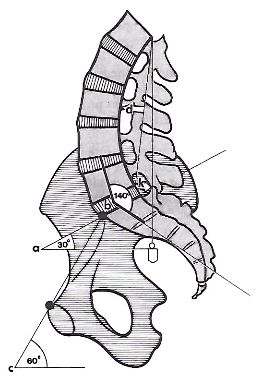
a: angle of sacrum
b: lumbosacral angle
c: angle of pelvic tilt
d: index of lumbar lordosis
The direction of the processus articulares superior are directed postero-medial, the processus articularis inferior are directed antero-lateral.
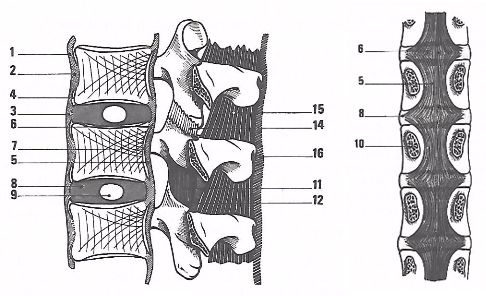
1 ligamentum longitudinale anterior
2 ligamentum longitudinale anterior
3 lig longitudinale anterior connecting to discus intervertebralis
4 potential place for osteophyts
5 ligamentum longitudinale posterior
6 short arched fibres connected to the discus intervertebralis
7 space for venae-network
8 discus intervertebralis
9 nucleus intervertebralis
10 pediculus
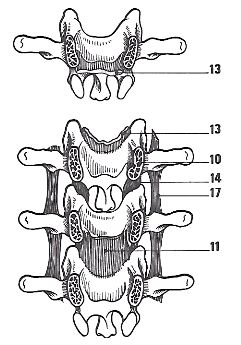
11 ligamentum flavum
12 ligamentum flavum
13 ligamentum flavum
14 capsular and the antero-medial ligaments
15 ligamentum interspinosus
16 ligamentum supraspinosus
17 ligamentum intertransversarium
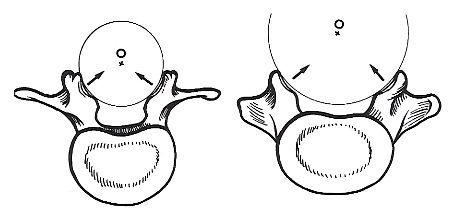
Left: Higher Lumbar Vertebra Right: Lower Lumbar Vertebra
The Lumbar Vertebral Column, Rotation
Geometrically speaking the profiles of the articular facets correspond to a cylinder with axis O.
It must be stressed that the center of this cylinder does not coincide with the center of the vertebral plateaus. The rotation of the upper vertebra resembles a sliding of the upper corpus vertebra upon the lower.
The shearing forces involved and the form of the processus articularis limit the range of rotation segmentally and globally. Total rotation of the Lumbar Vertebral Column is bilaterally 10 degrees, which is 2 degrees per segment and a unilateral 1degree of rotation. The Lumbar Vertebral Column is not built for axial rotation.